Powder coating for industrial products
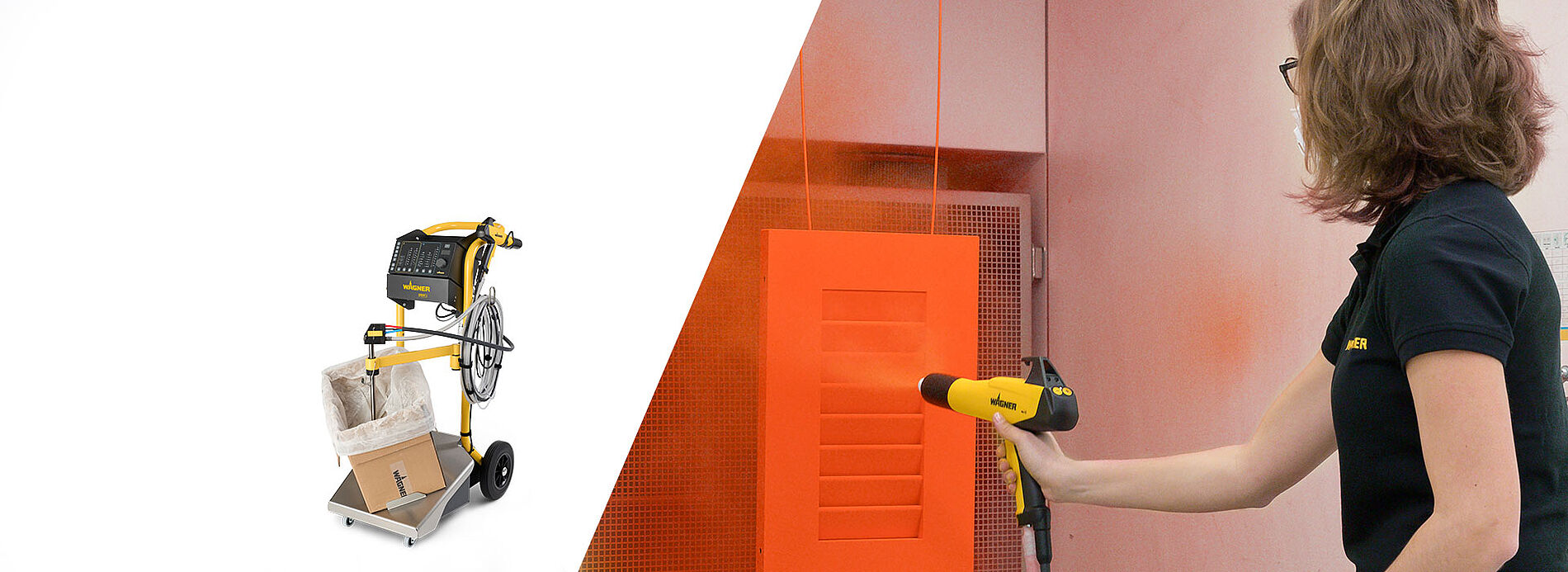
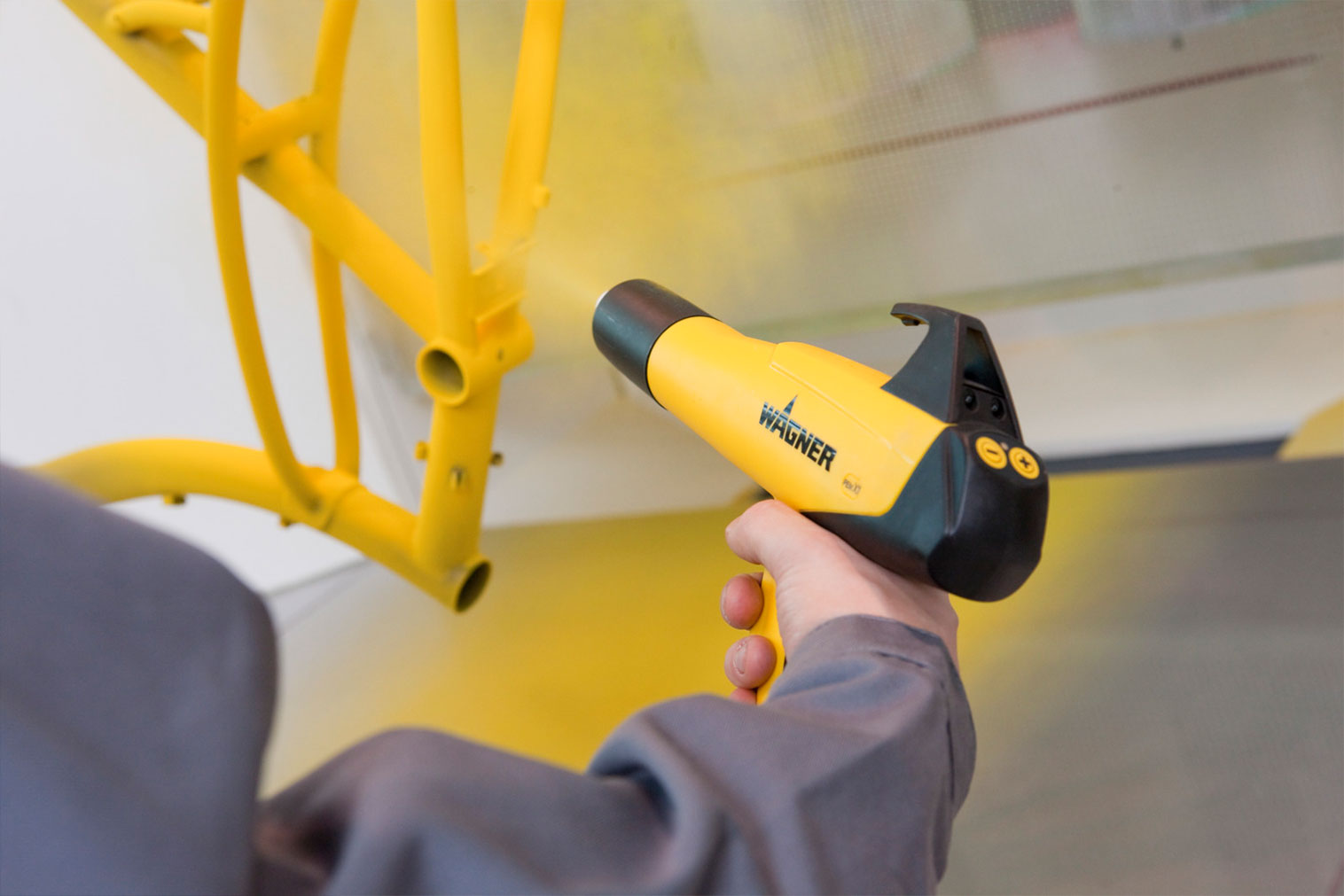
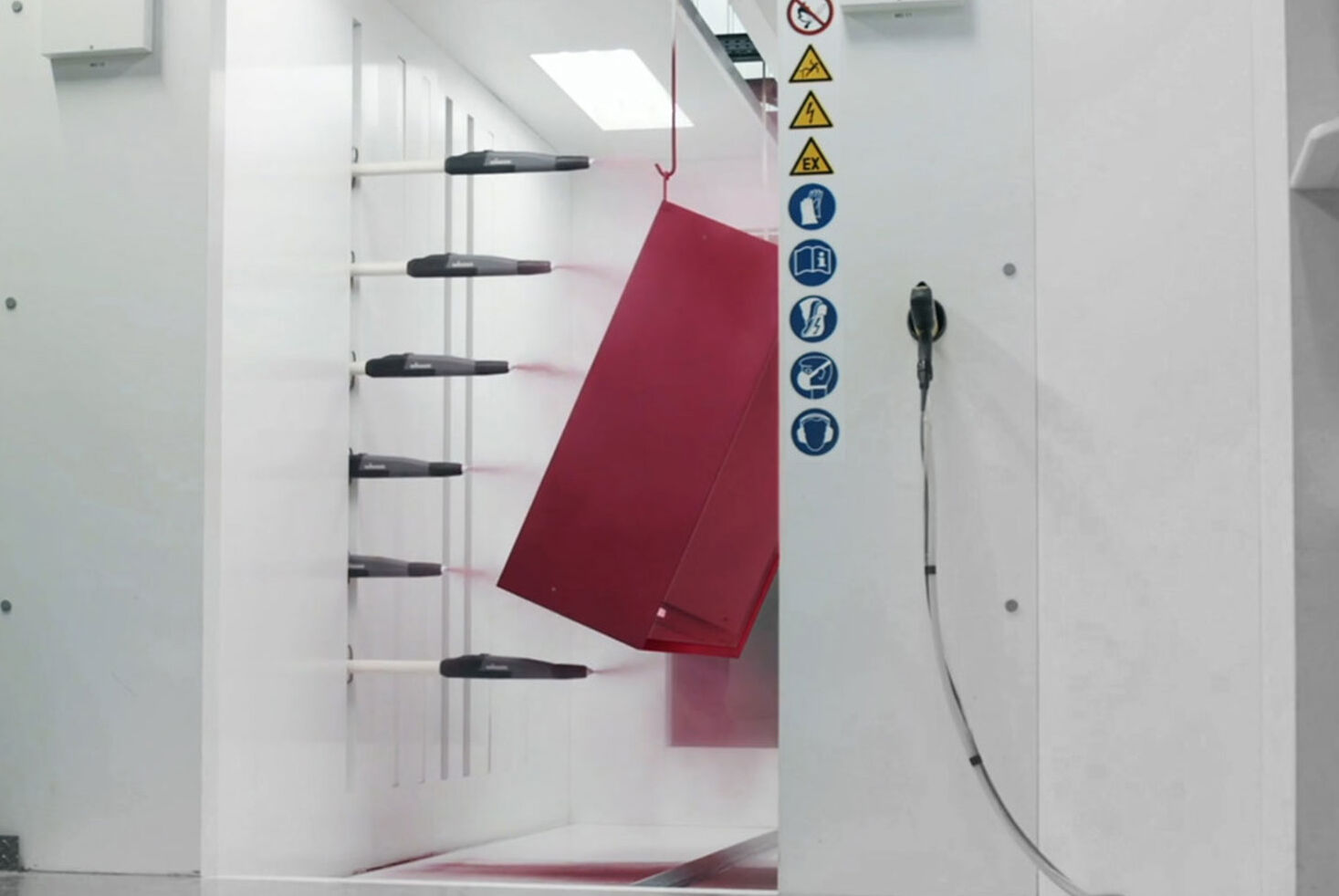
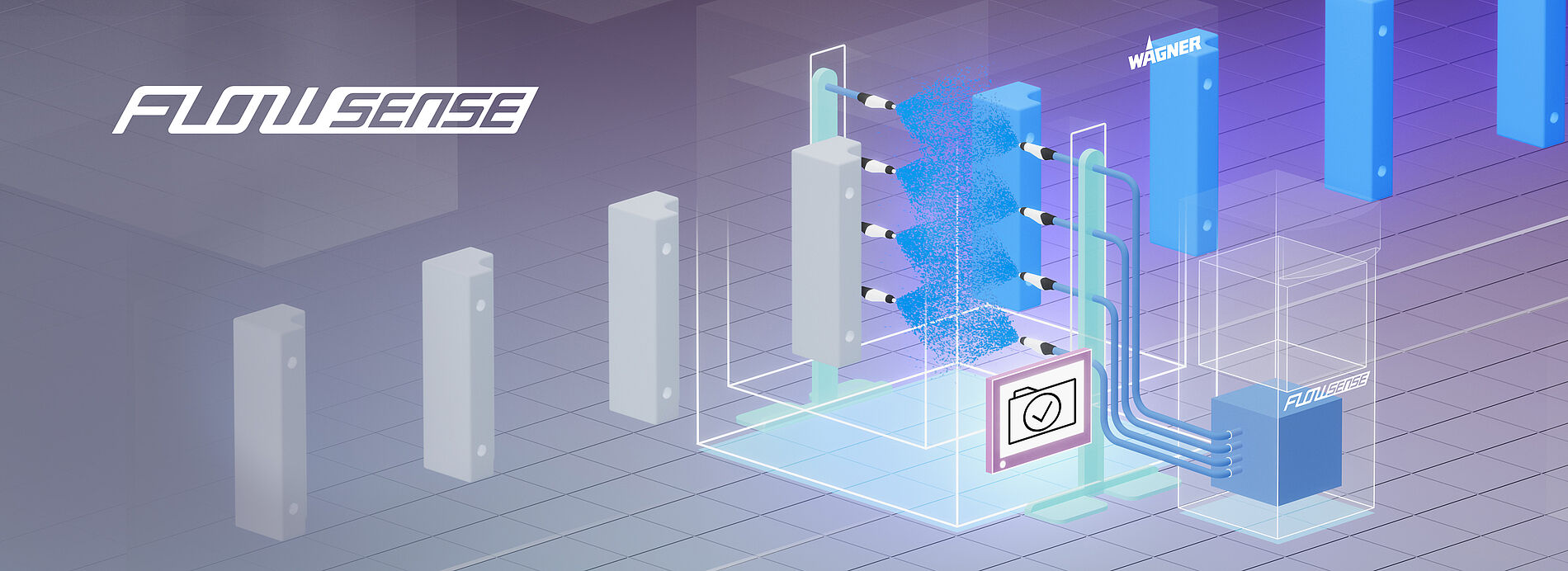
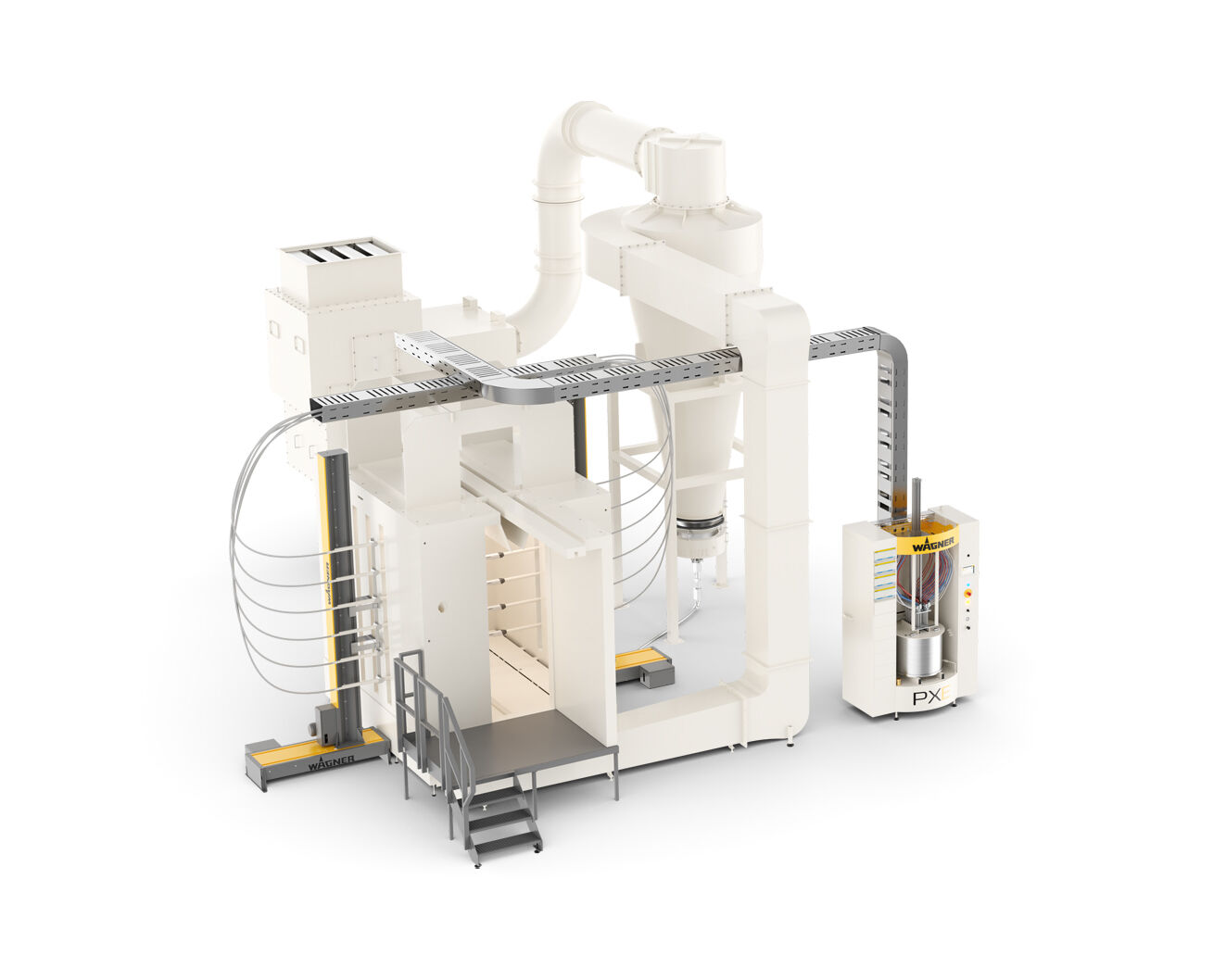
Powder coatings enable first-class coatings for a wide range of surfaces. Important success factors in industrial powder coating are an excellent look and feel of the coating layer, long durability, high economic efficiency of the process and sustainable use of resources. Powder coating offers a wide range of colors and surface effects.
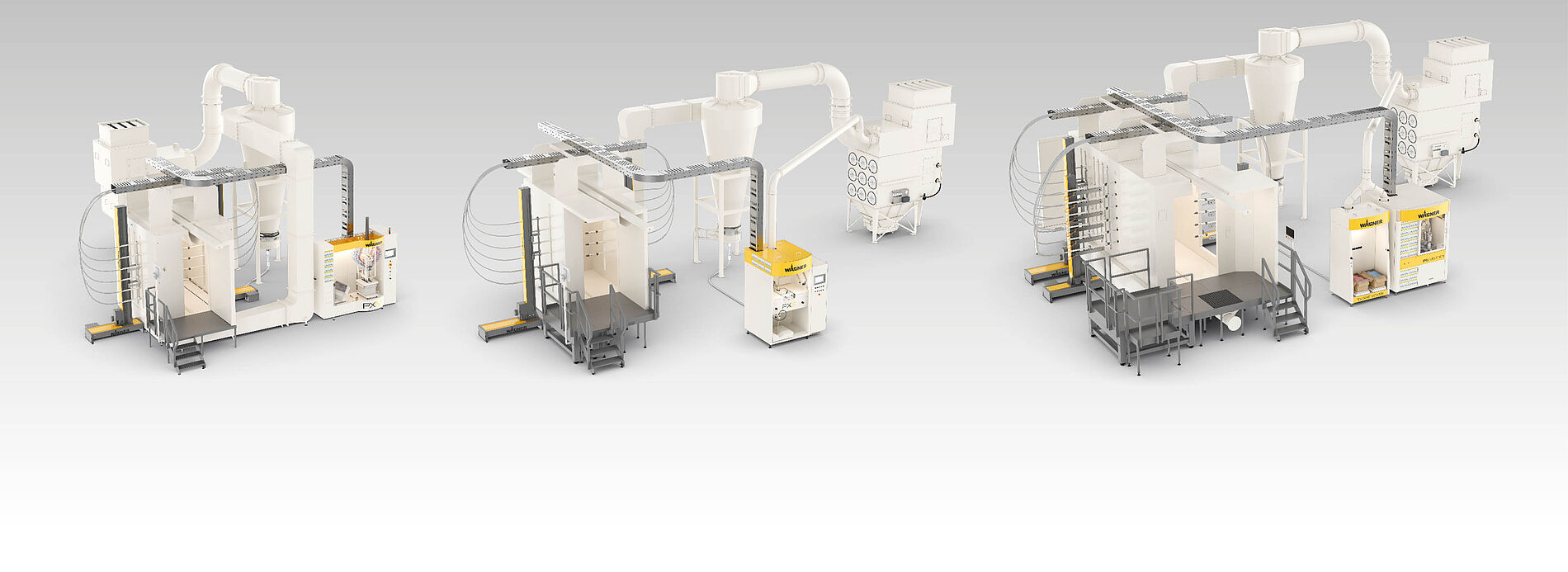
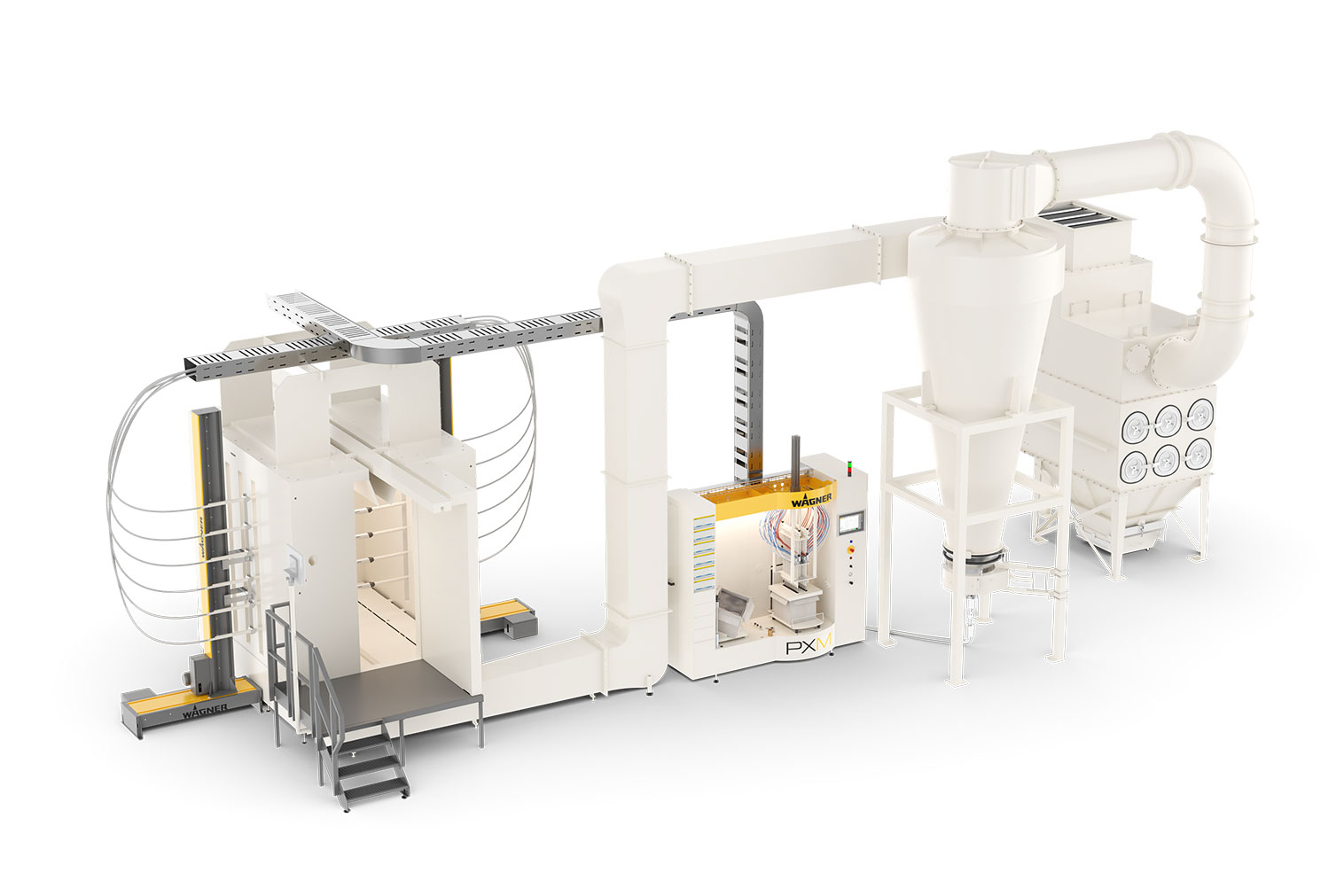
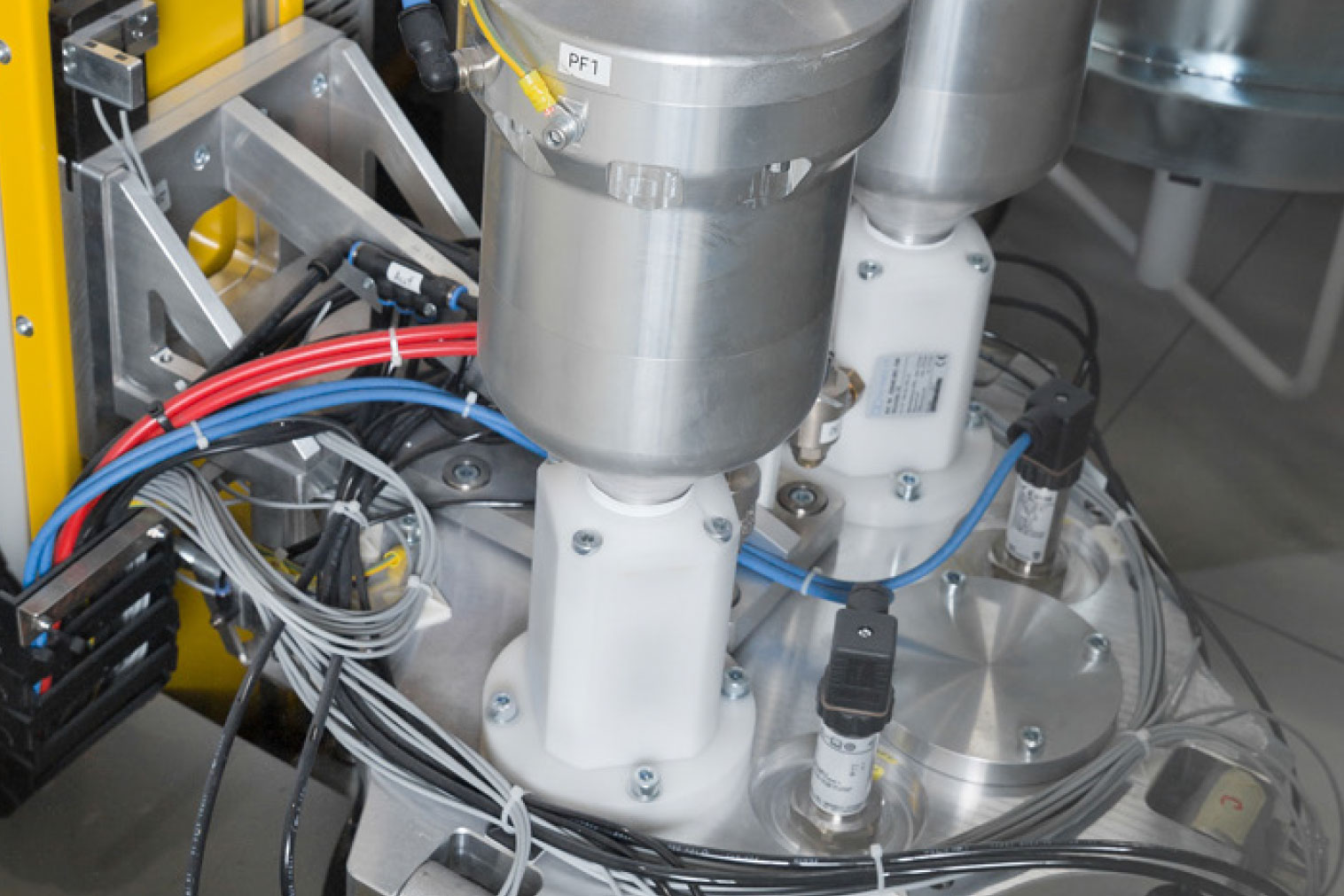
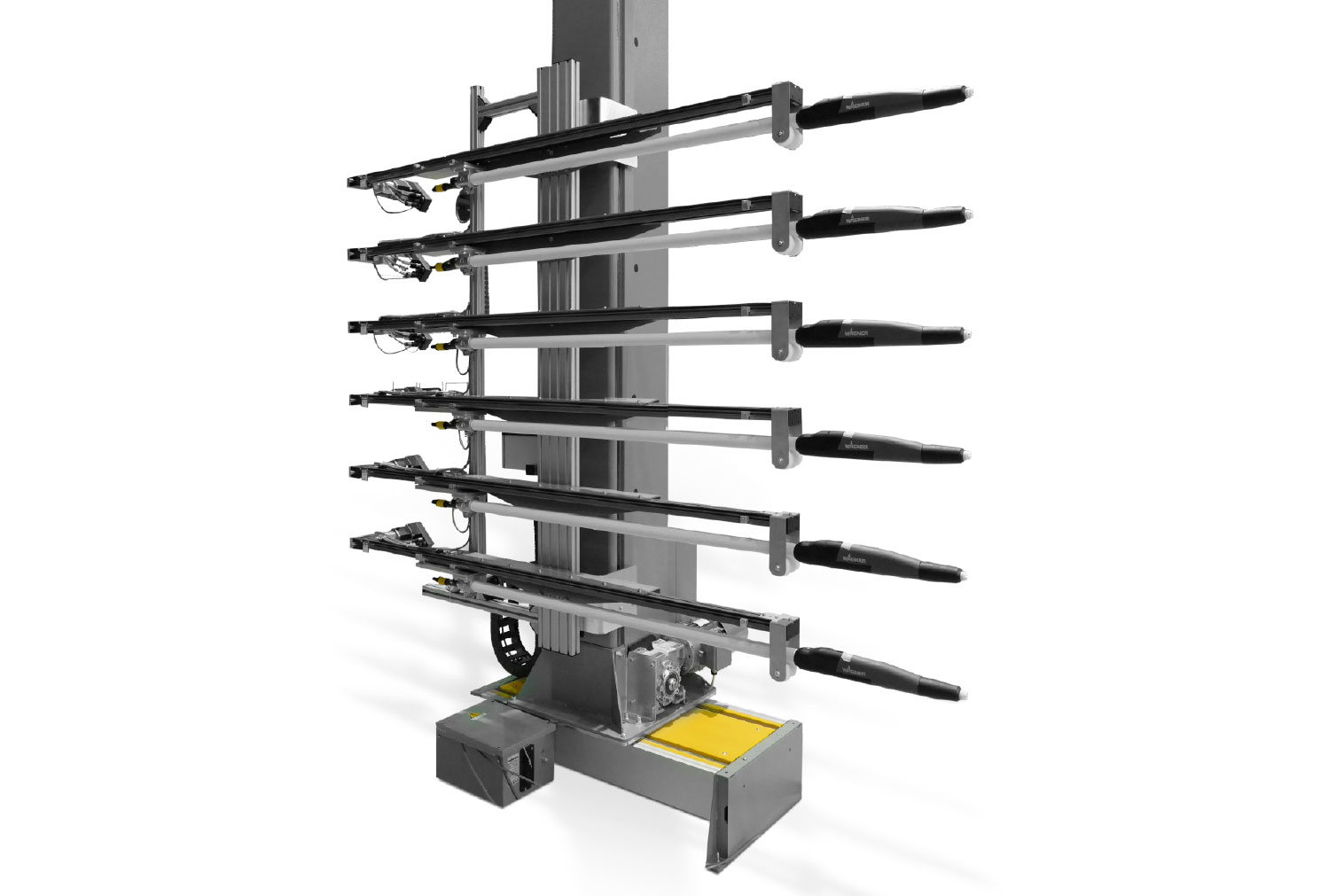
WAGNER offers highly efficient standard products and customized solutions. From products for manual coating to complex systems for automatic powder coating. Standardized or customized to your application. Our products and systems offer versatile application possibilities, fast color change if required, and efficient process technology for feeding, applying and powder recovery.